Oral Anomalies In Newborns: An Observational Cross-Sectional study
Presented this paper in dentist mt gravatt, pure dentistry in Sep 2019 this article was prepared by de Oliveira, Duarte et al 2019
I read somewhere in an article that there are 621,000,000 untreated caries in kids worldwide. Untreated caries in adults is estimated to be 21,000,000,000 caries worldwide.
In 2004, Harris said there were 106 risk factor for caries. Just some interesting estimates by others before I start this presentation.
Recap
- breastfeeding and association with malocclusion
- exclusive breastfeeding less than 6 months may be associated with malocclusion
- various factors involved in malocclusion so very hard to find association with cross sectional studies
Rationale


Introduction
- high frequencies of oral anomalies in newborns
- some anomalies may need treatment and some just follow ups
- limited experience in diagnosis of abnormalities
Patil, Rao et al. 2016
Aim of Study
- prevalence of oral anomalies in newborns and the influence of maternal and neonatal factors on the development of these anomalies
Methods
- cross-sectional observational study
- hospital and Maternity Ward Dom Orione (HMDO)
- ethics approved
- INCLUSION CRITERIA
- Full term newborns (37-41 weeks and 6 days)
- Stayed with mother in the same room
EXCLUSION CRITERIA
- craniofacial anomalies
- systemic conditions/intensive care
- incomplete data
- normal approximation for propagation using Wald, CI of 95%
- 30% max prevalence of oral anomalies in other studies
- 20% added to allow for losses
- kappa 0.81
- one examiner
- pilot study
- use of glove, disposable wooden tongue depressor, flashlight if needed
Discussions
-
- other studies: 41.2% and 42.9% overall prevalence
De Leon-Tapia et al, Correa et al.
- most prevalent :Palatine cyst, alveolar cyst, eruption cyst, neonatal teeth and ankyloglossia
Perez et al.
Results
- 55.2% female newborns
- mean weight: 3301 g
- mean length 50.1 cm
- 61% vaginal birth
- 58.2% mother 20-29 yrs
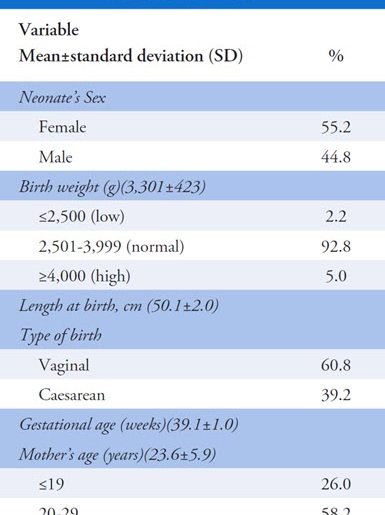
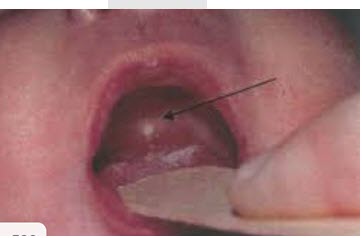
- anomalies in 50% of neonates
- 43% palatine cysts
- 26% alveolar cysts
- 9% ankyloglossia
- 2 neonates had congenital eruption cyst
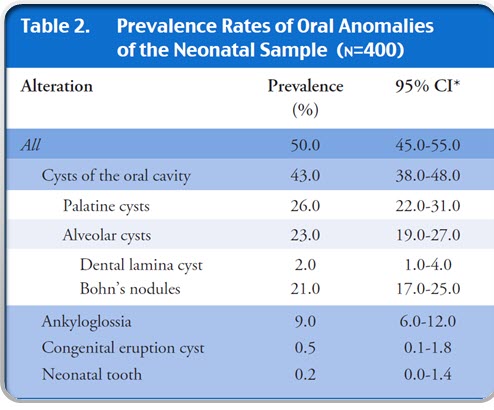
no statistically significant differences regarding the distribution of alveolar cyst, palatine cyst and ankyloglossia and sex and weight at birth of infants and maternal age and type of birth
palatine cyst
- most prevalent
- median palatine raphe
- posterior at junction on soft/hard palate
- not at pre-maxilla area (first portion to fuse, cysts degenerated
Friend et al. 1990, Correa et al.1998
Alveolar cysts
- Mostly multiple
- Vestibular portion of upper gingival mound
- Lower prevalence compared to palatine cysts
- No clinical manifestations
Cataldo et al. 1968
Difference between studies
- diagnostic/evaluation criteria
- sample variation
- cyst definition
Centinkaya et al. 2011
- ethnic factor higher prevalence in white children (2.5-folds higher)
- cysts in neonates
- not well understood
- may resolve spontaneously
- auto marsupialization
- no intervention
- Ankyloglossia
- 9% present study
- lack of agreement on evaluation/classification
- 11%- Frendenberger et al.
- 1.72% Jorgenson et al.
- 4.4% Friend et al.
- 2.5% Flink et al.
- natal and neonatal teeth
- female
- one in 376 to one in 3000
Freudenberger et al. 2008, Prabhakar et al. 2009, Mhaske et al. 2103
- eruption cysts
- 0.5%
- central incisor
- not very common and similar to other studies
- treatment : careful evaluation of clinical and radiographic finding
- no statistically difference between the frequency of alveolar and palatine cyst and birth weight similar to other studies
Cetinyaka et al. 2011, Jorgenson et al. 1982
- lower prevalence of alveolar and palatine cysts in preterm and low-birth-weight infants (later examination )
Donely et al. 2000, Monteagudo et al. 2012
Conclusion
- 50% prevalence of oral anomalies
- no correlation between anomalies studied and maternal and neonatal variables
Critique-Title/Abstract
- title includes type of study
- abstract is a good overview of the article. Purpose, methods, results, conclusion clear
- no description of the anomalies
- different names that may be used
- common sites
- keyword: cysts, prevalence, maternal and neonatal factors
Critique Method
- analytic study?
- mum and child that stay in the same room?
- good exclusion criteria for neonates
- exclusion data for mums?
- type of hospital
- 30% was not the highest prevalence, in study by Jorgenson et al. the prevalence was 64%
Analytic study search for why and how, causes and effect, this is was mostly just observational and not looked in to the cause
does it matter for mum and child to stay in the same room? If yes not explained
If parents had a genetic disorder/ systemic issues, can that effect the prevalence?
Is this a low social economic hospital? Could it be more randomized, going to different hospitals different parts of the city
- undersize sample compared to other studies
- N=2,021 / 500/ 2,258/ 1000
- all examinations done in 48 hrs
- principal investigator?
Study by Cetinkaya N=2021
Fiend GW N=500
Jorgerson et al N=2258
Montegudo et al N=1000
Who was the principal investigator? Specialist? Any consensus for the definition of the anomalies? How did they identify a lsion as alveolar cyst?
- more than one examiner to reduce bias
- pilot study
- good description of which areas were examined
- maternal factors: age/type of birth
Good to have pilot study
Maternal factors: just age and type of delivery? How about systemic conditions and smoking etc….they have used Cetninkaya et al as a reference and they had concluded that there was statistically significant relationship between the oral lesions and congenital diabetes, insulin trx during pregnancy and smoking during pregnancy and gestational diabetes.
- mostly- tables easy to understand
- table 2-alveolar cyst
- dental lamina cyst
- Bohm’s nodule
Has not been described about this in the text
- limitations: different diagnostic, evaluation and sample variation, cyst definition
- Photos
- what did they consider as ankyloglossia
They have outlined this as a limitation but have not tried to make any changes in their study to allow for it, maybe chose studies that have looked at the same description of the cyst?
Take home message
- oral anomalies of newborn are very common
- need to be able to identify them
- reassure parents
- usually no treatment needed
Epstein’s Pearls
- epithelial remnants trapped along line of fusion
- posterior palate
- small keratinized cysts
- raised nodules
- no treatment
- 30%-60% different article
Bohn’s Nodules
- remnants of dental lamina
- labial/buccal of alveolar ridge in maxilla
- About 40%
- No treatment
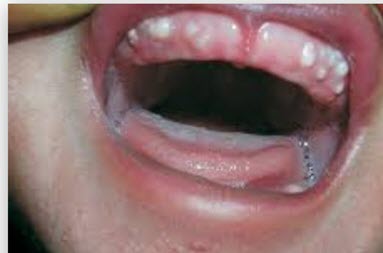
Congenital Epulis
- congenital epulis. pedunculated, soft nodule from 1 mm to several cms in diameter located on gingival margin, proliferation of mesenchymal cells . Very low prevalence les than 1 %. Usually in Maxilla
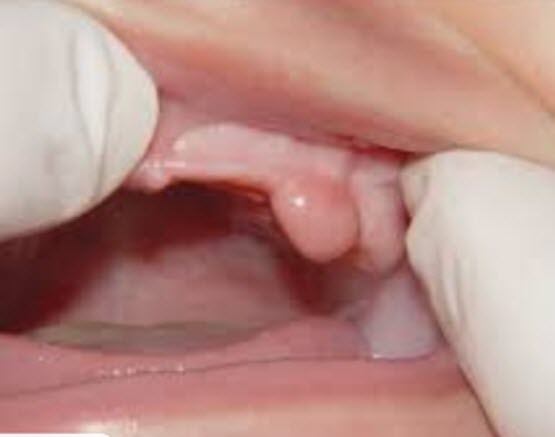
Melanotic Neuroectodermal tumor of infancy
- melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy
- neural crest cells
- maxilla
- swelling of mucosa, bluish black color or pink
- high recurrence rate
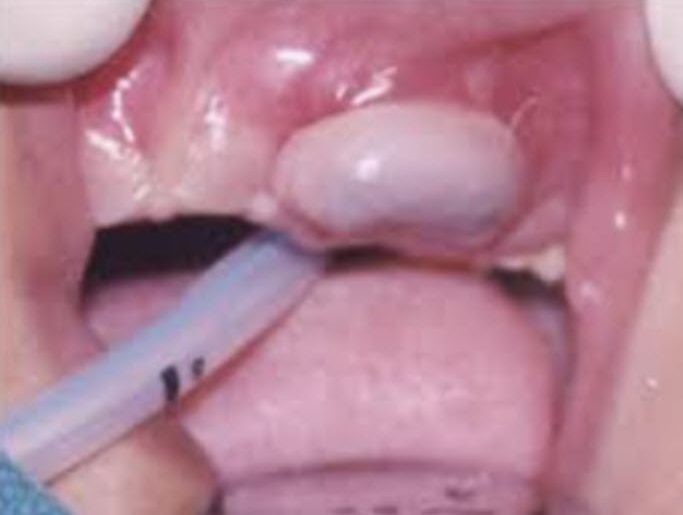
Alveolar Lymphangioma
- alveolar lymphangioma
- 3-4% in back population
- alveolar ridge
- fluid filled-bluish
- spontaneous regression
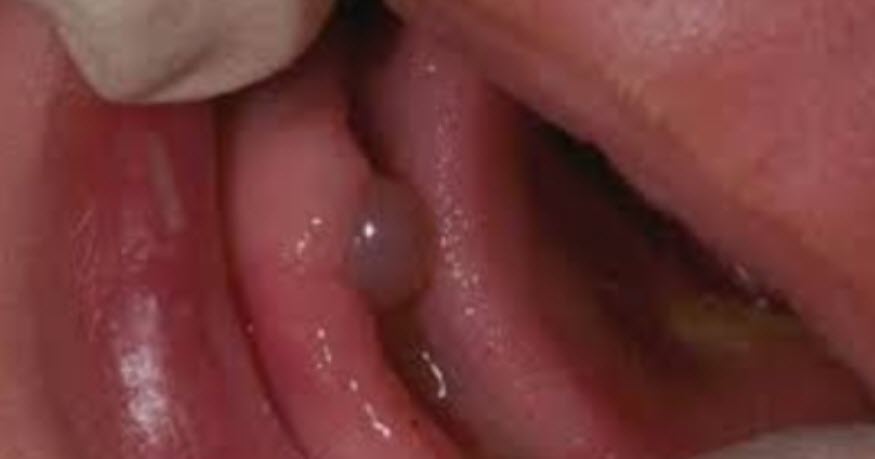
Congenital Ranula
- congenital ranula
- floor of mouth, lateral to lingual frenum
- mucous extravasation cyst damage to submandibular or sublingual ducts
- less than 1%
- excision
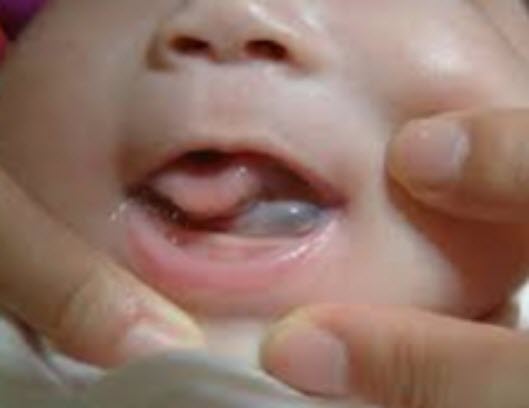
Giant Cell Tumor
- primary dentition, dark purplish, alveolar crest
- benign
- hyperthyroidism
- needs to be excised
- Central or peripheral
Normal approximation for proportions using wald confidence
is a confidence interval for the probability of success calculated from the outcome of a series of success–failure experiments. In other words, a binomial proportion confidence interval is an interval estimate of a success probability p when only the number of experiments n and the number of successes nS are known.the binomial proportion is defined as the number of successes divided by the number of trials
known to have a bad performance for small to medium sample size
Standard error
The standard error of a statistic is the standard deviation of its sampling distribution.
Standard deviation: a quantity expressing by how much the members of a group differ from the mean value for the group
Chi square test
A chi-squared test, also written as χ2test, is any statistical hypothesis testwhere the sampling distribution of the test statistic is a chi-squared distribution when the null hypothesis is true. The chi-squared test is used to determine whether there is a significant difference between the expected frequencies and the observed frequencies in one or more categories.
Fisher exact test
The Fisher Exact test tests the probability of getting a table that is as strong due to the chance of sampling. The word ‘strong’ is defined as the proportion of the cases that are diagonal with the most cases. The Fisher Exact testis generally used in one tailed tests.
Used in smaller samples